Key Facts on Arachnoid Cysts
- An arachnoid cyst is a relatively common condition that can occur at any age but is often detected in children and adolescents.
- While generally not dangerous or cancerous, arachnoid cysts can cause complications if they grow large enough to exert pressure on surrounding brain structures.
- Arachnoid cyst symptoms vary depending on location and size of the lesion.
- Diagnosis is primarily achieved through imaging studies, with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT) scans being the most effective methods.
- Treatment options include conservative monitoring for asymptomatic cases and surgical interventions such as cyst fenestration or shunting for more severe or symptomatic cases.
What is an Arachnoid Cyst?
An arachnoid cyst is a fluid-filled sac that forms within the arachnoid layer, which is one of the three membranes (meninges) that cover and protect the brain and spinal cord. These cysts contain cerebrospinal fluid and are benign, originating from developmental anomaly.
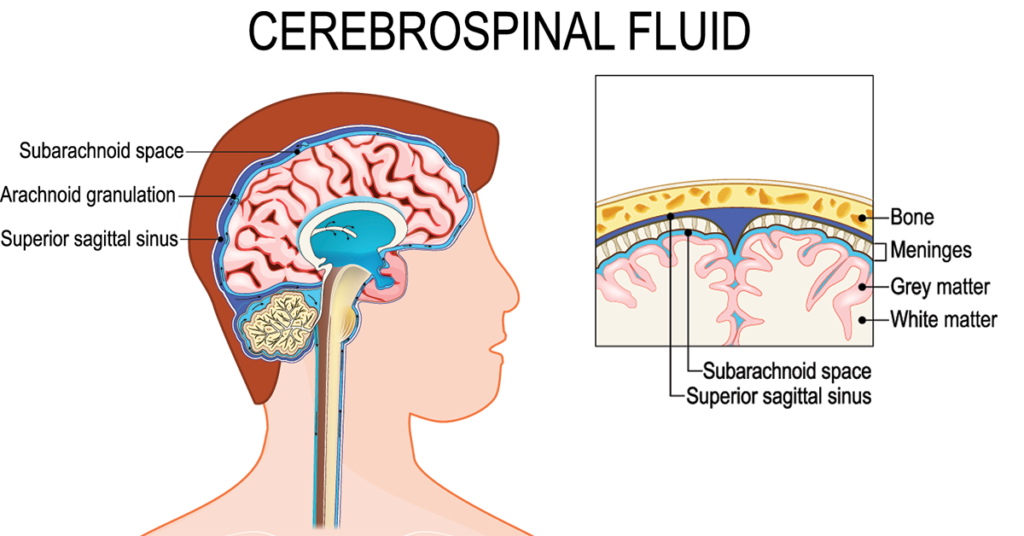
They can emerge in various areas of the brain and spinal cord and might remain asymptomatic or manifest symptoms such as headaches, nausea, and balance issues. Arachnoid cysts are often discovered incidentally during imaging for unrelated reasons. They can occur in individuals of any age but are most frequently diagnosed in children and adolescents.
Are Arachnoid Cysts Dangerous?
Understanding the potential risks is crucial for individuals diagnosed with this condition. While arachnoid cysts are generally benign, certain complications can arise, influencing the approach to treatment and management.
Can These Cysts Be Cancerous?
These cysts are benign, meaning they are non-cancerous and do not metastasize or spread to other parts of the body. These cysts are filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and are enclosed by the arachnoid membrane, distinguishing them from tumors or cancerous growths. The primary concern with arachnoid cysts is not their potential for malignancy but the effects they may have on surrounding brain or spinal cord tissue due to their size or location.
Can Arachnoid Cysts Burst?
They can, though it is a rare occurrence. If the arachnoid cyst ruptures into the cranial or spinal space it essentially cures the disease. If however, they rupture outside central nervous system the cerebrospinal fluid leakage develops. A burst arachnoid cyst can lead to the release of cerebrospinal fluid into surrounding areas, potentially causing symptoms such as severe headaches, nausea, seizures, or sudden changes in neurological function. Arachnoid cyst rupture symptoms require immediate medical attention to prevent complications and manage the leakage of CSF.
Can These Cysts Grow?
These cysts can grow, but not like tumors. The cerebrospinal fluid is entrapped in the cyst. The cyst can grow if fluid can enter but not exit the cavity. Some cysts remain stable in size for years, while others may grow slowly or, in rare cases, more rapidly. Factors influencing growth include the cyst’s location and the individual’s age. Regular monitoring through MRI or CT scans is essential to track changes in the size of the cyst and address any potential issues promptly.
Are Brain Cysts Life-Threatening?
While arachnoid cysts themselves are typically not life-threatening, complications arising from large or deep cysts can pose significant health risks. Complications such as cyst rupture, significant pressure on brain structures, or the development of hydrocephalus (accumulation of fluid in the brain) can have serious, potentially fatal outcomes if not treated promptly. However, with appropriate medical management, including timely intervention, most individuals with arachnoid cysts lead normal, healthy lives.
Symptoms and Signs
Arachnoid cysts can manifest a range of symptoms depending on their size and location. Symptoms can be particularly concerning when they occur in children or affect daily activities.
What Symptoms Can an Arachnoid Cyst Cause?
The symptoms of arachnoid cysts can vary widely. Headache is a common complaint, characterized by persistent or intermittent headaches that can vary in intensity. The nature of these headaches can provide clues about the cyst’s location and whether it’s affecting brain function or fluid dynamics. In children, symptoms might also include nausea, lethargy, or developmental delays. Severe cases might manifest as seizures or significant changes in cognitive functions.
Can Arachnoid Cysts Cause Behavior Problems?
Arachnoid cysts can influence behavior, especially in children. When the cyst exerts pressure on certain parts of the brain, it can lead to changes in behavior or cognitive functions. Parents might notice unusual irritability, mood swings, or changes in personality in their child.
Diagnosis: Identifying Size and Location
Diagnosing arachnoid cysts accurately determines the appropriate course of treatment and the potential impact on an individual’s health. Modern imaging techniques such as CT scans, MRIs, and ultrasounds play a critical role in the identification and assessment of these cysts, focusing particularly on their size and location.
What Size Arachnoid Cyst Is Considered Large?
In the context of cysts, size matters significantly. A cyst is generally considered large if it is larger than 3 cm. The arachnoid cyst size chart is a tool that healthcare providers use to categorize cysts into small, medium, or large. Large cysts are more likely to cause symptoms due to the pressure they exert on surrounding brain tissues or the obstruction of cerebrospinal fluid flow.
Where Are Arachnoid Cysts Located?
These cysts can be found anywhere within the cranial and spinal subarachnoid spaces, which are the areas between the brain or spinal cord and the arachnoid membrane. Common locations include the middle cranial fossa, sylvian fissure, posterior fossa, and around the spinal cord. Precise localization through imaging is crucial for determining the potential effects of a cyst on neurological function and developing an appropriate treatment plan.
Middle Cranial Fossa
These cysts are commonly found within the brain’s intracranial spaces and can impact surrounding neurological structures. This may lead to a variety of symptoms, including headaches, seizures, or specific neurological deficits. Cases involving a left middle cranial fossa arachnoid cyst or its counterpart on the right can specifically alter cognitive and sensory functions, requiring careful monitoring and management.
Retrocerebellar and Posterior Fossa
Similarly, cysts located in the retrocerebellar or posterior fossa regions pose unique challenges. These cysts can impact cerebellar function, leading to balance issues, coordination difficulties, and other cerebellar signs. Retrocerebellar arachnoid cysts and those in the posterior fossa are particularly noteworthy for their potential to affect cerebrospinal fluid dynamics, possibly leading to hydrocephalus or intracranial pressure changes.
Arachnoid Cyst in Spinal Cord
Arachnoid cysts can develop along the spinal cord and require specialized treatment approaches. Cysts, located within the arachnoid membrane that covers the spinal cord, can manifest in any part of the spine but are predominantly found in the thoracic and lumbar regions. Spinal cyst treatment is tailored to the cyst’s size, location, and the presence or absence of symptoms.
The spinal cyst, particularly when located in the lumbar spine, may cause symptoms such as lower back pain, sciatica, or neurological deficits depending on its size and the pressure it exerts on adjacent neural structures. In contrast, cysts in the thoracic spine might lead to symptoms like mid-back pain, sensory disturbances, or even myelopathy, a condition affecting the spinal cord.
What Does an Arachnoid Cyst Look Like on an MRI?
On an MRI, the cyst appears as a well-defined, fluid-filled sac that is similar in intensity to cerebrospinal fluid on both T1 and T2 weighted images. Its borders are typically smooth, and it does not enhance with contrast, distinguishing it from other types of cysts or brain tumors.
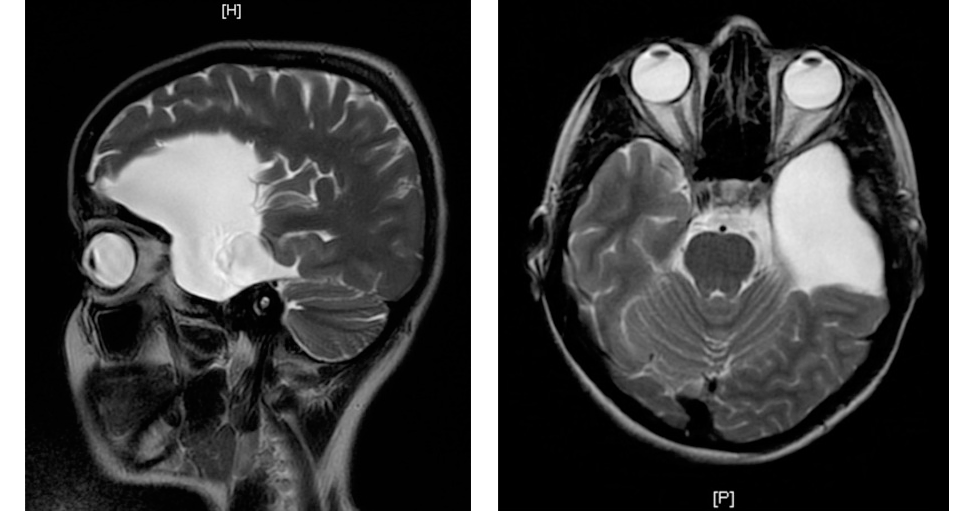
The clarity of MRI imaging allows for the detailed visualization of the cyst’s relationship with adjacent brain structures, aiding significantly in the assessment of its impact. While CT and MRI are the mainstays of diagnosis, arachnoid cyst ultrasound can be useful, especially in pediatric patients or in the initial assessment of cysts in the brain or spinal cord.
Treatment Options
The choice of treatment is highly individualized, considering factors such as the patient’s overall health, symptom severity, and cyst characteristics. Treatment strategies include:
Watchful waiting: This approach is viable for asymptomatic cysts, with regular monitoring to track any changes in size or onset of symptoms.
Fenestration: A minimally invasive surgical technique where a window is created in the cyst to allow the fluid to drain into the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and relieve the pressure.
Shunting: Implanting a shunt system to divert the cyst’s fluid into another area of the body, such as the abdominal cavity, where it can be absorbed.
Surgery: What to Expect
Surgery is a significant procedure undertaken to alleviate symptoms caused by cysts or to prevent potential complications. This treatment option is considered when cysts are symptomatic, growing, or located in areas that could affect critical brain functions. The surgery aims to remove or reduce the cyst and improve the patient’s quality of life.
Types of Arachnoid Cyst Surgery
The two primary surgical methods for treating arachnoid cysts are fenestration and shunting. Fenestration of cysts involves creating openings in the cyst to allow cerebrospinal fluid to escape to the surrounding brain or spine areas, where it can be absorbed. This method can relieve pressure symptoms. Arachnoid cyst removal is more invasive and involves excising significant portion of the cyst wall and establishing broad connection with normal CSF pathways. The bigger the communication the lesser the chance for later occlusion and recurrence.
Shunting is another option used to treat arachnoid cysts. During shunting the fluid from the cavity is diverted into other body areas (usually peritoneal cavity) for absorption.
The choice between fenestration and shunting depends on the cyst’s location, size, and the symptoms it causes.
Recovery Time
Arachnoid cyst surgery recovery time varies among individuals. In adults, the typical recovery period can range from a few weeks to several months, depending on the surgery’s extent and the patient’s overall health. Recovery time is crucial for the body to heal and for the patient to gradually return to daily activities.
Surgery Cost
Arachnoid cyst surgery cost can vary based on the surgical approach and hospital stay length. It’s essential for patients request a consultation about their condition to understand the details.
📅 Interested in arachnoid cyst treatment options and surgery costs? Request a consultation with Dr. Kamran Aghayev to get clear answers and a personalized care plan.
Success Rate
The arachnoid cyst surgery success rate is generally high, with many patients experiencing symptom relief and a return to normal activities. However, as with any surgery, the details should be discussed thoroughly with a medical professional.
Finding an Arachnoid Cyst Specialist
Treatment of arachnoid cysts may require a specialized medical approach. If you are looking for a specialist in arachnoid cysts, please contact our clinic: Dr. Aghayev’s expertise guarantees effective treatment, individual approach and careful attention to your specific case.
For those interested in learning more, we invite you to watch a video of Dr. Kamran Aghayev performing an arachnoid cyst fenestration operation.
References
- White M.L., Das J.M. Arachnoid Cysts. StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf. 2024.
- Fam M.D., Woodroffe R.W., Helland L., Noeller J., Dahdaleh N.S., Menezes A.H., Hitchon P.W. Spinal arachnoid cysts in adults: diagnosis and management. A single-center experience. Journal of Neurosurgery. 2018.
- Pradilla G., Jallo G. Arachnoid cysts: Case series and review of the literature. Neurosurgical FOCUS. 2007.
- Epigenomic dysregulation correlates with arachnoid cyst formation and neurodevelopmental symptoms. Nature Medicine. 2023.
- Gangemi M., Seneca V., Colella G., Cioffi V., Imperato A., Maiuri F. Endoscopy versus microsurgical cyst excision and shunting for treating intracranial arachnoid cysts. Journal of Neurosurgery. 2011.